Spinal Decompression
A non-invasive alternative to spine surgery
A non-invasive alternative to spine surgery
The BTL SPINAL DECOMPRESSION is a mechanical therapy that uses automated decompressive forces to mobilise joints, relieve the pressure over neuro-spinal structures, and relax and elongate soft tissues.
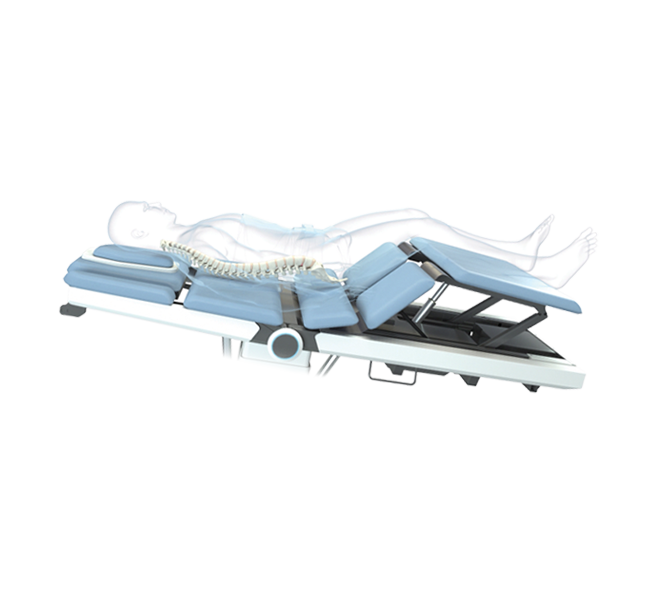

The BTL SPINAL DECOMPRESSION promotes a new way forward to precise
targeting of the therapy into impaired segments of the spine and innumerable
options for the treatment of lower back pain of any origin.
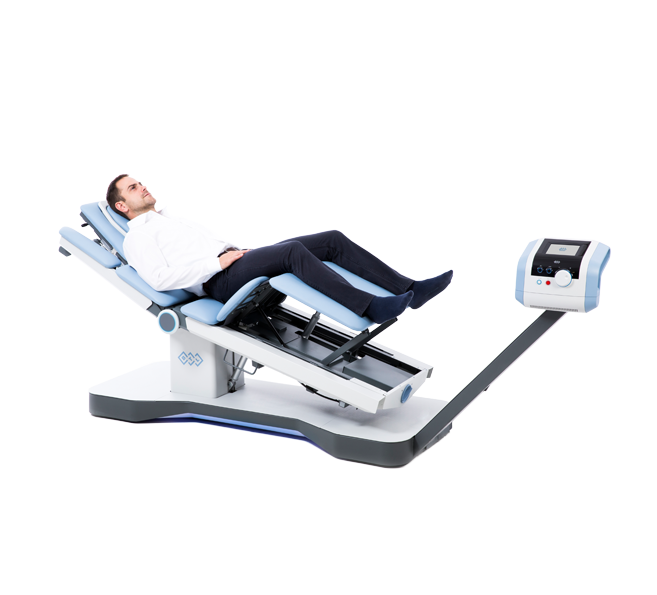
We produce the very first automated decompression for neck pain that
perfectly substitutes manual therapy without compromising clinical outcomes.

Get in touch with us if you want the newest technology to improve patient care.
Not all products and indications may be licensed in your country. For more information, contact your local representative.
In the EU, the following products are registered under different names:
Focused Shockwave (BTL-6000 FSWT), Radial Shockwave (BTL-6000 RSWT), Super Inductive System (BTL-6000 Super Inductive System), High Intensity Laser (BTL-6000 High Intensity Laser), TR-Therapy (BTL-6000 TR-Therapy), Spinal Decompression (BTL-6000 Traction and BTL Spinal Decompression), Cryotherapy (BTL Cryotherapy), HandsFree Sono ( (BTL-4000 Smart / Premium); Combined Units (BTL-4000 Smart / Premium), Electrotherapy with vacuum unit (BTL-4000 Premium + BTL-Vac II), Low-Level Laser Therapy (BTL-4000 Smart / Premium), Magnetotherapy (BTL-4000 Smart / Premium), Combined Units (BTL-4000 Smart / Premium), Diathermy (BTL-6000 Shortwave and BTL-6000 Microwave), CPMotion (BTL-CPMotion), Lymphatic Drainage (BTL-6000 Lymphastim), Couches (BTL-1100, BTL-1300, BTL-1500), Hydrotherapy (BTL-3000)
We will contact you as soon as possible.